FCSS, Ò.8, ¹4, 2007
Abstracts
M.A.Ruvinskii1, B.M.Ruvinskii2
Effect of Magnetic Field on
Hypersonic Attenuation by Electrons
in Rectangular Quantum Wire
1Vasyl Stefanyk' Precarpathian
National University,
57 Shevchenko Str., Ivano-Frankivsk, 76000, Ukraine
2Ivano-Frankivsk National Technical University of Oil and Gas,
15, Carpatska Str., Ivano-Frankivsk, 76000, Ukraine,
bruvinsky@gmail.com
The effect of quantum magnetic
field on attenuation of the lowest width mode of hypersound by electrons in a
rectangular quantum wire is theoretically investigated. The energetic spectrum
and the wave functions of electrons in rectangular wire at the high
longitudinal magnetic field have been determinated. The magnetic and
dimensional dependencies of electron hypersonic attenuation in wire have been
obtained. The numerical results have been presented for the case of GaAs wire.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (327kb)
Yu.
Skorenkyy, O.Kramar
Peculiarities of the Antiferromagnetic Ordering in a
Model of Quasi-Onedimensional Organic Superconductors
Ternopil State Technical Uneversity, 56, Ruska St.,
Ternopil, UA- 46001, Ukraine, E-mail: skorenky@tu.edu.te.ua
Within the single-electron retarded Green function
method, with use of effective Hamiltonian in configurational representation the
transition from antiferromagnet to paramagnet state in narrow-band
low-dimensional system has been studied. The form of effective exchange
parameter zJeff/w which govern the antiferromagnetic
order stabilization in quasi-onedimensional system with strong Coulomb correlation
has been found. At increase of zJeff/w the temperature
of the phase transition (Neel temperature) increases rapidly. The calculation
of phase (p-T) diagram of antiferromagnet-paramagnet transition for the
system (TMTSF)2PF6 has been carried out. The obtained
results agree with experimental data.
Key words:
quasi-onedimensional superconductors, antiferromagnetic ordering, effective
exchange, correlated hopping of electrons.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (311kb)
V.I. Boichuk,
I.V. Bilynsky, I.O. Shakleina
The Dispersion of the
Coefficient of Reflection from the Interface of a One-Dimensional Crystal
Heterosystem
Ivan Franko Drohobych State
Pedagogical University,
24, Ivan Franko Str., Drohobych, UA–82100, Ukraine,
e-mail: ioshak@mail.ru
In the paper a three-layer nanoheterostructure
with a transitive layer at the separation boundaries is
described by a Kronig-Penney model
with
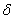 –function potentials. The distance
between the farthest atoms of the transitive layer is a parameter of the
problem and ranges from zero to two lattice parameters of crystals. An exact
solution is obtained for the reflection coefficient
–function potentials. The distance
between the farthest atoms of the transitive layer is a parameter of the
problem and ranges from zero to two lattice parameters of crystals. An exact
solution is obtained for the reflection coefficient 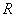 which
makes it possible to determine the dependence of the factor on
a wave vector, widths of a transitive layer and a monolayer of the nanoheterostructure. The specific calculations performed for the
which
makes it possible to determine the dependence of the factor on
a wave vector, widths of a transitive layer and a monolayer of the nanoheterostructure. The specific calculations performed for the  heterosystem showed
that the envelope-function approximation and the effective mass method at small values of a wave vector
yields quite good results provided the Harrison boundary conditions are used with appropriately chosen parameters.
heterosystem showed
that the envelope-function approximation and the effective mass method at small values of a wave vector
yields quite good results provided the Harrison boundary conditions are used with appropriately chosen parameters.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (317kb)
V.A. Romaka1,2, M.G. Shelyapina3, D. Fruchart4, Yu.V. Stadnyk5,
Yu.K. Gorelenko5, L.P. Romaka5, V.F. Chekurin1
Conductivity Features of the n-ZrNiSn
Intermetallic Semiconductor Strongly Doped with Mn. I. Electronic Structure
Calculation
1Ya. Pidstryhach Institute of Applied Problems of Mechanics and
Mathematics National Academy of Scieces of Ukraine,
Naukova Str. 3-b, 79060 Lviv, Ukraine;
2National University
“Lvivska Politechnika”, Bandera Str. 12, 79013 Lviv, Ukraine;
3V.À. Fock Institute
of Physics, St.-Petersburg State University,
Ulyanovskaya Str. 1, Petrodvorets, 198504,
St.-Petersburg, Russia;
4Laboratoire de
Cristallographie, CNRS, BP 166, 38042 Grenoble Cedex 9, France;
5Ivan Franko Lviv
National University, Kyryl ànd Mephodiy Str. 6, 79005 Lviv, Ukraine
Calculations of the electronic
structure of the ZrNiSn intermetallic semiconductor, strongly doped with the
acceptor impurities of Mn, were carried out. The calculations were performed
for the paramagnetic and ordered distribution of the Mn atoms. Doping of the n-ZrNiSn semiconductor results in a change of
conductivity from electron to hole-type and realization the transition of
conductivity insulator-metal (Anderson transition). Thus,
the conductivity of semiconductor is determined mainly by the Mn d-electrons
and exclusively with spin-down directed. A total magnetic moment linearly
depends on the concentration of acceptor impurities of manganese, while the
magnetic moment of Mn atoms quite quickly becomes saturated and practically
unchanged for dopant concentrations x over 0.1.
Key words: semiconductor; acceptor impurity; Fermi level; electrical
conduction; density-of-states.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (368kb)
V.A. Smyntyna, O.A. Kulinich, M.A.
Glauberman, G.G. Chemeresuk,
I.R. Yatsunskiy, O.V. Svyridova
The
Influence of Defects on Distribution of a Dopant Concentration and Defect
Formation at Silicon Doping
I.I. Mechnikov National University,
Marshala Govorova Str, 4, Odessa, 65063, Ukraine,
E-mail: eltech@elaninet.com
In this
paper the influence of defects on distribution of a dopant concentration on a
surface and on depth of monocrystal silicon wafers are given. It set, that this
distribution of impurity on a surface is connected to the distribution of
oxygen concentration which, in turn, is connected to structure of silicon
wafers.
The
silicon doping result in occurrence of structural defects as dislocation nets
in silicon wafers which precipitated oxygen and, it was not observed aggregations of a
dopant about dislocation nets with concentration exceeding medial.
Key
words: silicon, doping,
defects, dislocation.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (358kb)
P.D.
Maryanchuk, D.P. Kozyarskyy, E.V. Ìàistruk
Physical Properties of Crystals (3HgSe)1-x(Al2Se3)x,
Doped by Manganese
Yu.Fedkovych Chernivtsi National University, M.
Kocubynsky Street, 2,
58012 Chernivtsi, Ukraine (037)22-4-68-77, emaistruk@list.ru
Researches of kinetic factors of
crystals (3HgSe)1-x(Al2Se3)x (doped by manganese) are carried out during the interval Ò = 77 - 300 Ê and
Í = 0,5 - 5 kOe before and after the thermal treatment of samples in vapour
components. Before the thermal treatment factor of the Hall (RH) in
researched crystals does not depend on temperature, electroconductivity (σ) crystals
has metal character, thermoelectric motive power (α) increases with
the growth of temperature. Thermal treatment of samples in vapour components
results in the change of the electrons concentration.
Magnetic susceptibility of
(χ) crystals (3HgSe)1-x(Al2Se3)x (doped by manganese) is investigated at the interval of temperatures Ò = 77 - 300 K at Í = 4 kOe by
the method of Faraday before and after the thermal treatment of samples in
vapour components. It is established, that features χ are caused by the
presence in crystals of such clusters as Mn-Så-Mn-Så, of different
size, in which the indirect exchange interaction of antiferromagnetic character
between the Mn atoms through the atoms of chalcogenide is carried out, and the Mn atoms with 3d4 and 3d5 electrons configuration.
Thermal treatment of samples in vapour components results in the change of the
size of existing crystal clusters and in the change of the electrons configuration
of Mn atoms from 3d4 to 3d5.
Key words: crystal, electroconductivity, magnetic susceptibility,
cluster.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (315kb)
Z.I. Zakharuk1, S.G. Dremlyuzhenko1, M.L. Koval’chuk1, E.S. Nikonyuk2 A.I. Rarenko1
Researches of the Si Phase
Inclusions in CdTe,
Cd1-xMnxTe, Cd1-xZnxTe Crystals
1‘Yuriy Fedkovich’ Chernivtsi National University, 2, Kotsyubynskiy Str.,
Chernivtsi,
58012, Ukraine, MLKov@mail.ru
2National University of Water Management and Conservation, 11,
Soborna Str, Rivne,
33028, Ukraine, semirivne@mail.ru
The present paper deals with the
results of surface heterogeneity researches of the CdTe, Cd1-xMnxTe,
Cd1-õZnõTe crystals by the x-ray and metalografic
methods. By the scanning electronic microscope-microanalyzer it is shown, that these
heterogeneities are often Si inclusions. They are heterogeneous and have, as a
rule, Al, O, Fe, Cr, S, Cl, Mg. The contamination of
material by Si occurs by quartz transferring from the region of capillary making for the
evacuation of ampule. The
high density of Si inclusions leads to the strong
heterogeneity of the electro-physical properties of material.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (1Mb)
G.E. Davidyuk, V.V. Bozhko, G.L. Mironchuk
Influence of Surface of
Standard on the Machineries of Formation of Defects at the Electronic
Irradiation of Specially Unalloyed and Alloyed by a Copper Monocristal of
Sulfide of Cadmium
Volin state university,
13, Volya Av., Lutsk, 43025, tel. (803322) 4922
e-mail: ftt@lab.univer.lutsk.ua
In work specially unalloyed and
alloyed by a copper monocrystal CdS were explored. The irradiation of standards
by electrons with E = 1,2 MeV (by a
dose Ô = 2×1017 ål/ñm2)
conduces to formation of mobile at a room temperature defects, and also, disintegration
of initial donor – acceptor associates. More radiation monocrystal CdS turned
out firm. Primary radiation defects in CdS:Cu – standards
(NCu = 1018 cm-3) form after the irradiation the
second defects which act part of rapid centers of recombination and accountable
for admixture photoconductivity. At saving of the exposed crystals to the rays
in their near a surface region paramagnetic centers are formed. Conclusions
about nature of the second radiation defects of accountable for photoactive and
paramagnetic centers in the exposed standards to the rays are drawn.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (335kb)
Ya.V. Zaulychny, Yu.M. Solonin, S.S.
Zviezda, E.V. Pryluckij
Dependence
of Energy Distribution of Valence Electrons of Carbon Nanomaterials in
Different Atomic-Structural
States on Their Sizes
Frantsevych Institute for
Problems of Materials Science,
National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, 3 Krzhyzhanivsky Str., Kiev UA-03142, Ukraine, zaulychnyj@ipms.kiev.ua
Ultra-soft x-ray emission
spectroscopy was applied to study the electronic structure of a number of
carbon nanomaterials. The energy distribution of valence electrons was
investigated in fullerenes, onions and multi-walled nanotubes obtained using
catalysts and without them. It was found that the width of the ÑKα-bands
somewhat increases in the following sequence C60-C70-onions-nanotubes.
Narrowing the spectra was revealed when decreasing sizes of nanomaterials of
the same kind. It was established that shapes of the ÑKα-bands in C60,
C70, onions, nanotubes are different due to changing
the degree of πðz-
and σsp2+ πðz-overlapping.
Key
words: fullerene, carbon onion, nanotube,
electronic structure, x-ray emission spectrum, valence band, hybridization
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (403kb)
M.
Kharchenko
Using of Closed Box Deposition
Technique for Preparation of Cadmium Telluride Thin Films
National
technical university”Kharkiv polytechnic institute”, Kharkiv, 21 Frunze Street,
61002.
The definition of critical
temperature of condensation of ÑdTe vapor in closed box on glass and ceramic
substrates at evaporator temperature 420 – 560îÑ was carried out. At the
indicated temperature range at a minor vapor supersaturation a single-phase
ÑdTe films were obtained. The increasing of formation temperatures resulted in
changing of grain preferred orientation from (111) to (110) at simultaneous
improvement of structural quality
Key words: thin films, cadmium
telluride, closed box deposition technique, structural quality
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (299kb)
I. Voynarovych1, V. Takach2,
V. Cheresnya1, V. Pynzenik1, I. Makauz1, S. Chernovich1,2
Amorphous Chalcogenide-Metal
Multilayers
1Institute of Solid State Pysics and Chemistry, University of
Uzhgorod,
Pidhirna Str.46, Uzhgorod, 88000, Ukraine,
phone +38 031 22 32485, e-mail: sse@univ.uzhgorod.ua
2Institute of Physics, University of Debrecen, Bem
ter 18/a, Debrecen, 4026, Hungary,
phone +36 52 415222, e-mail: viki@delfin.unideb.hu
Bi(Sb)/As2S3 nanomultilayers (NML) were developed
and produced with different modulation periods in the 4-10 nm range using the computer-controlled
cyclic vacuum evaporation technology. The influence of the thermo- and/or
photo-induced interdiffusion on the optical parameters and electrical
conductivity were investigated in such model nanostructured materials in order
to establish the possibilities of surface pattern recording and to develop the
method of solid phase synthesis which allows to create
materials nanostructured at different scales.
Key words: nanostructures, multilayers, interdiffusion, optical and electrical
characteristics.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (400kb)
D.M. Freik, B.S. Dzundza,
V.M. Chobanyuk
Profiles of Electric Parameters in the
Thin Films of Lead Chalcogenides
Vasyl
Stefanyk PreCarpathian National University,
57, Shevchenko Str., Ivano-Frankivsk,
76000, Ukraine, E-mail: fcss@pu.if.ua
Profiles effective and local value
of electric parameters in epitaxial n- and p- type PbTe, PbSe growen from
vapour phase are explored. It is shown, possibility
of creation in films of n-types conductivity of
two-layer n-p-structure, the parameters of which are determined by composition
of preforms, and also temperatures of evaporation and deposition and after by
condensation processes.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (1.5Mb)
G.I. Kopach1, N.P.Klochko1,
N.D.Volkova2, M.V. Dobrotvorskaya3,
V.R. Kopach1, T.A.Li1
Mechanism of the Electrochemical Deposition Process and Composition of
Cadmium Telluride Films
1National Technical University (Kh PI), 21,Frunze Str., 61002,
Kharkiv, Ukraine
2National Aerospace University (KhAI),17, Chkalov Str., 61070,
Kharkiv, Ukraine
3Monocrystal Institute, National Academy of Sciences, 60, Lenin Av., 61001, Kharkiv, Ukraine
E-mail: li_tatiyana@mail.ru
The
mechanisms of electrochemical processes in the electrolyte for obtaining of
cadmium telluride semi-conducting films and in corresponding partial solutions
contained ions of cadmium and tellurium were investigated by voltammetric
analysis with lineal potential scanning and by cyclic voltammetric analysis
methods. The differences between cathodic processes on chemically inert
titanium nitride substrates and on catalytically active molybdenum surface were
revealed. On the base of these investigations the nature of impurities was
discovered in this work by X-ray
photoelectron spectroscopy on molybdenum and titanium nitride surfaces and in
the volume of cadmium telluride films was explained. The last allowed choosing
the parameters of the electrodeposition process and the substrate material,
which provide stoichiometric composition of the films.
Key
words: cadmium
telluride, X-ray photoelectron
spectroscopy, voltammetric analysis, cyclic voltammetric analysis
methods.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (333kb)
S.A Nedilko, T.A. Voitenko,
M.A. Zelenko, M.O. Obolenskiy1,
V.I. Biletskiy1,
M.M. Chebotaev1
High
Temperature Superconducting Ceramic in the Systems
Bi2-xLnxSr2CuO6+z (Ln-La, Nd,
Y)
Taras
Shevchenko Kyiv National University, Department of Chemistry,
Volodymyrska str., 60, 01033, Kyiv, Ukraine, nedilko@univ.kiev.ua
*Karazin Kharkiv National University, Department of Physics,
Svobody sq, 4, 61077, Kharkiv, Ukraine
The
samples Bi2-xLnxSr2CuO6+z (Ln-La, Nd,
Y) were synthesized using the ceramic technique with precursor. For Bi2-xLnxSr2CuO6+z (Ln-La, Nd,
Y) a homogeneity region, phase composition, structural parameters, oxygen
stoichiometry and magnetic susceptibility depend on their composition (x) and Tcon
value was study.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (276kb)
Y.Y. Obedzynska, P.
M. Fochuk, Z. I. Zacharuk, I. M. Yuriychuk, O. E.
Panchuk
Influence of Bi on the Electrical
Properties of CdTe Under Cd Vapor Pressure
Chernivtsi National University,
2, Kotziubinskoho, 58012, Chernivtsi, Ukraine
Å-mail:
fochuk@chnu.cv.ua
At first the experimental results
of detailed Hall effect measurements at
high-temperature defect equilibrium under Cd vapour pressure in CdTe<Bi>
single crystals were performed. They indicate that at these conditions Bi forms
in CdTe crystals BiCd donor centres. The analysis of the free
electron density temperature dependencies allows to conclude
that an essential quantity of Bi-containing precipitates in the CdTe lattice exists. The study of
high-temperature electrical properties in Bi-doped CdTe samples shows that the
real electrical active Bi content in the investigated crystals is at some 700 K ~1×1016 at/cm3, whereas at higher temperatures point defect
structure modelling indicates the possibility of the rise of electrical active
Bi centers content due to partial dissolution of Bi precipitates in the
crystal.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (384kb)
S.G. Dremlyuzhenko,
Z.I Zakharuk, P.M. Fochuk, A.I. Savchuk
Change
of Defect System and Surface Composition of CdTe,
Cd1-xMnxTe, Cd1-õZnxTe Crystals at
Treatment
Yuriy Fedkovych
Chernivtsi National University, 2 Kotsjubynskyi Str.,
Chernivtsi 58012, Ukraine Tel.
+380-372-584893, e-mail: sgdrem@mail.ru
The
mechanism of oxide films formation and surface
composition of CdTe, Cd1-xMnxTe, Cd1-õZnxTe
samples are determined on the base of
thermodynamic calculations and Auger-electron spectroscopy studies. Samples surface composition was investigated after various
treatments: chemical etching with Br2
solution in methanol; chemical and mechanical polishing in solution comprising
K2Cr2O7 and HNO3; chemical and
mechanical polishing in alkaline solution of colloidal silica. Chemical
and mechanical polishing in alkaline solution of colloidal silica allows
obtaining high-purity surface of good quality with a minimum violation of
stoichiometry.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (429kb)
S.S.
Novosad, B.M. Kalivoshka
The Electret Properties of CdI2:ÑuI
Photochromic Crystals
‘Ivan Franko’ Lviv National
University, 50, Dragomanov Str., Lviv, 79005, Ukraine
å-mà³l: novosadss@rambler.ru
The
electret properties of CdI2:Ñu² photochromic crystals, grown by
Bridgmen-Stockbarger method, has been investigated by capacitor method with insulating contacts. The
polarization current, caused by sample’s oneside cooling in the dark from 295
to 90 K, was found out. The crystal polarized during it oneside cooling
owns the photosensitivity in the near edge spectrum region. The CdI2 activation by copper impurity
leads to the change of polarization and depolarization currents direction of
thermogradient electrical state, formed in crystal during it oneside cooling, and weakens
the material’s photosensitivity, connected with F-type centers, in the infrared
spectrum region. It was found out that the electret state is formed in CdI2:ÑuI crystal at the room temperature during it colouration
by integral lighting of DKsEl lamp at the absence of external electrical field.
The presence in the sample of intrinsic electrical field such the photochromic
electret state leads to the change of polarization and depolarization currents
directions of thermogradient electrical state. The possible mechanizm of
colouring and uncolouring of photochromic CdI2:ÑuI crystals have been discusion.
Full text (on original language).pdf (335kb)
S.S. Novosad, I.S. Novosad
The photo- and thermostimulated processes in photochromic CdBr2:Cu
crystals
‘Ivan
Franko’ Lviv National University,
Franko Lviv National University, 1, Universytetska Str., Lviv, 79000, Ukraine,
tel. (0322) 964-679, e-mail: novosadis@rambler.ru
The photo- and thermostimulated
processes in photochromic CdBr2:Cu, CdBr2:Cu,Cl, CdBr2:Cu,I, crystals grown by the Bridgman-Stockbarger method have been studied.
It was established, that the concentration of copper impurity, the temperature
and also the homology anion impurity are influenced on the efficiency of
photochemical transformations (PCT) in CdBr2:Cu+ crystal. It was supposed, that appearance of unstructured additional background absorption in the region of transparency after
the optical irradiation of samples of weakly alloyed CdBr2:Cu crystals is conditioned by
photodecomposition of lightsensitive {(V2–Cd – VI+)–Cd³+}
centers. The PCT in cadmium bromide with considerable concentration of copper
impurity are caused by change of charge state of activated centers. The complex
{(Cu+Cd)––Cui+} centers
are decayed and Cu2+Cd-centers and nCu0
colloids are created in such crystals under irradiation of UV-light from the
region of photosensitive. In strong alloyed systems the kinetic of photostimulated
process of coloring besides the change of charge state of activated centers also are determined by the conditions of irradiation as a results of the change of optical properties and the
thickness of irradiation layer of CdBr2:Cu. The reverse process of
thermal uncoloring of crystal are taken place through oxidation of Cu0-centers
by Cu2+Cd ions with the help of migration process of
holes thermodelocalizated from divalent copper ions through anion sublattice to
colloid metal parts.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (402kb)
Magdalena Popczyk
The Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on
Electrolytic Ni+W+Si and Ni+W+Mo+Si Composite Coatings
University of Silesia, Institute of Materials Science,
Bankowa 12, 40-007 Katowice, Poland e-mail: magdalena.popczyk@us.edu.pl
Ni+W+Si and Ni+W+Mo+Si composite coatings
were obtained by electrolytic codeposition of crystalline nickel from an
electrolyte containing suspension of suitable metallic and non-metallic
components (W, Mo and Si). These coatings were
obtained under galvanostatic conditions, at the current density of jdep.
= 0.100 A•cm-2 and at the temperature of 338 K. Chemical composition of obtained coatings was
determined by EDS method. The electrochemical activity
of these coatings was studied in the process of hydrogen evolution reaction
(HER) from 5 M KOH solution using steady-state polarization and electrochemical
impedance spectroscopy (EIS) methods. Basing on the results of EIS measurements
the rate constants of the HER were determined. It was
found that Ni+W+Mo+Si composite coatings are characterized by enhanced electrochemical activity towards hydrogen
evolution as compared with Ni+W+Si coatings. The reason of this is connected with the
presence of additional composite component (molybdenum). Thus obtained coatings may be useful in application as
electrode materials for the hydrogen evolution reaction.
Key words: Nickel, Tungsten, Molybdenum, Silicon, Composite coatings, Hydrogen
evolution reaction.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (312kb)
V.D.
Alecsandrov, O.V. Sable, M.V. Savencov
Research of the Before Crystallization
Supercooling
in the System Water - Pentahydrate Sodium Thiosulfate
Donbass national academy of
building and
architecture
2, Dergavina Str, Makiivca, 86123, Ukraine, E-mail: cluck@mail.ru
The given work is devoted to experimental research of the before crystallization supercooling and character of crystallization of sample in the system
water - pentahydrate
sodium thiosulfate by the method of cyclic thermal
analysis.
Keywords:
crystallization, pentahydrate
sodium thiosulfate,
supercooling, cyclic thermal analysis.
Full text (on original language).pdf (480kb)
N.Vityuk1, A.Eremenko1 N.Smirnova1 , P.Gorbik1, T.Busko2,
M.Kulish2, O.Dmitrenko2, V.Shlapatska3, V.Higniy4
Influence of High-Energy Irradiation on the Structural and Photocatalytical Properties of Nanosized TiO2/ZrO2/SiO2 Composites
1 Institute of Chemistry of surface named by O.O. Chuiko NASU
17, Generala Naumova Str., Kyiv, UA-03164, Ukraine,
E-mail:annaerem@voliacable.com,
2Kyiv national university named by T.G.Shevchenko Kyiv, Ukraine
3BE «Radma» IPC NASU, Kyiv, Ukraine
4Institute physical chemistry named by L.V.Pysargevskyy NASU, Kyiv,
Ukraine
The high stable to β – irradiation
(Ee = 1.8 MeV) TiO2/ZrO2/SiO2 films
and powders were synthesized using sol-gel method from titanium, zirconium and
silicon alkoxides. The synthesized samples were monitored by SEM, XRD, EPR and
Raman spectroscopy. XRD data showed the formation of anatase with the 12 nm
crystals. The new signal with three g – factors: 2,009; 2,021 and
2,025 was appeared in EPR spectrum when the powders were caused by β – irradiation
with the dose 4 MGy relating to the oxygen vacancy. β – irradiation of the films and powders
lowers their photocatalytic activity in the process of photoreduction of Cr(VI)
toxic ions but it remains still high leading to the potential possibility of
the practical applications.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (546kb)
Z.Yu. Hotra1,2, P.Yu.Stakhira1,
V.V.Cherpak1, D.Yu. Volynyuk1
Investigation
of Electrooptical Properties of Polyorthometoxyaniline
Prepared by Thermovacuum Deposition
1Lviv Polytechnic National University, 12 Bandera St,.
Lviv, 79013, Ukraine
tel:
(032) 258-21-62, e-mail: stakhira@polynet.lviv.ua
2Rzeszów
University of Technology, Rzeszów, ul. W.Pola, 2, 35-95, Poland
Thin
films of polyorthometoxyaniline (POMA) were prepared by vacuum deposition at
pressure of 5•10–5 Torr and temperature range of 350-450 0Ñ.
The structure of vacuum deposited films was determined by method of infrared
spectroscopy. The morphology, optical and electrochromic properties of
deposited POMA thin films were studied.
Key
words: vacuum deposition,
polyorthometoxyaniline, infrared spectroscopy
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (300kb)
O.I. Konopelnyk1,
O.I. Aksimentyeva1, B.R. Tsizh2,3, M.I. Chokhan2
Physical-and Technological Properties
of the Sensor Materials Based on Conjugated Polyaminoarenes
1Ivan
Franko Lviv National University, Ukraine, 6 Kyryla-Mefodia, Lviv, 79005, Ukraine;
(0322) 728069; aksimen@ukr.net
2Stepan Gzytsky Lviv
National Academy of Veterinary Medicine, 50 Pekarska, 79012, Lviv, Ukraine
(0322)783635
3Kazimier Wielki University in
Bydgoszcz, 30 Chodkiewicza, Bydgoszcz, Poland, tsizhb@ukw.edu.pl
The physical and technological
properties (temperature dependence of conductivity, thermal stability, optical
absorption and structure) of the new sensor materials based on conjugated
polyaminoarenes such as poly-o-toluidine, polyaniline, poly-o,m-aminophenols have been studied in temperature
interval 273-773 K. It has been defined that change of inclination in
temperature dependence of conductivity is caused by thermal decomposition of
the polymers. The optical spectra of the polymer films exhibit an
interesting temperature behavior in the range 293- 473 K connected with
thermochromic transitions. By the X-ray powder
diffraction it has been found that polyaminoarenes are amorphous-crystalline
materials with content of crystalline phase from 20-22 % (undoped polymers) to
40-44 % (doped by inorganic acids) and with dimensions of crystallites 15-30
?. For the technology application of such materials the temperature
interval corresponded to the linear dependence of conductivity before the
thermal decomposition temperatures has been recommended.
Êëþ÷îâ³ ñëîâà: polyaminoarenes,
conductivity, thermal stability, thermochromic transitions,
structure.
Full text (on original language).pdf (468kb)
P.I. Melnyk, S.P. Novosyadly, V.M. Berezhansky, V.M. Vivcharuk
A Spectrometry in Submicron Technology of Large-Scale
Arrays
The Precarpathian National University, T.
Shevchenko Str., 57, 76025, Ivano-Frankivsk Ukraine,
e-mail: nsp@pu.if.ua, berezhansky@mail.ru, vivov@bigmir.net
A presence of atoms of basic
elements and admixtures in semiconductor, and also character of their division
in a volume determine the fundamental electrical and physical parameters of
structures of large-scale arrays. The control of composition of crystalline
structure gives primary information for subsequent researches of crystalline
and electronic structure, character of chemical connection, degrees of alloying,
imperfectness. The control of composition acts especially large part at the
decision questions of manufacturing the homogeneously alloyed layers and
crystals and crystals with the set concentration type in the active areas of
submicron structures. The analytical side of such researches is a spectrometry.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (521kb)
V.R. Petrenko1, V.A. Terban2, L. V.
Shepel1
Influence of Technological Parameters on Distributing of Oxygen
in the Silicon Single Crystal of Grown by Czochralski Method
1The Kremenchuk University of Economics, information technologies and
management,
24/37 Proletarska str., Kremenchuk, E-mail: pvr@ient.net
2Subsidiary 'Pure Metals Plant' of 'Pure Metals'
JSC, 3 Zavodskaya
str., Svetlovodsk
In the given work on the basis of
experimentally established dependences of speed of dissolution quartz crucible
in silicon melt from temperature and pressure of gas in the chamber cultivation
it is developed mathematical model of doping process of crystals of silicon by
oxygen. By means of model the estimation of sensitivity of initial (maximal)
concentration of oxygen in a crystal to fluctuations of the basic technological
parameters is lead. The received results allow to draw conclusions, that
average concentration of oxygen in a crystal is defined by average melt
temperature, and character of distribution of oxygen in a crystal depends both
on initial melt weight, and from the geometrical form of crucible, and also in
a smaller measure from diameter of a crystal.
Thus concentration of oxygen practically does not depend on dynamic
parameters of process of cultivation. Adequacy of the offered model is
experimentally confirmed by values of parameters of the crystals received in
real industrial conditions.
Key words: Czochralski method, distribution of oxygen, monocrystals of
silicon, mathematical model, concentration of oxygen, doping
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (459kb)
À.V. Besov1, À.V. Petryk2, P.I. Melnyk2
Physical-Chemical Conditions of Co-Cr-Mo-Ni Homogenous Powders Receipt With the Set Components Concentration
1Institutes of problems of material science the name of Frantsevicha
of NAS of Ukraine,
Krzhizhanivskogo Str., 3, Kyiv, 03680, Ukraine
2Precarpathion National University named after V. Stefanyk,
Shevchenko Str.,57, Ivano-Frankivsk, 76000, Ukraine, e-mail: ivan.petryk@rambler.ru, phone: +(03422) 59-60-80
The controlled technology of
chemical homogeneous Co-Cr-Mo-Ni powders receipt is developed and their
technological properties are obtained.
Keywords: oxides compounds, diffusive satiation
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (459kb)
O.V. Mannapova, A.D. Sokolov,
A.I. Kostrjitskijy
Physical-Chemical Properties of
Oxide Tapes
on Steel, Received by Ionic Bombardment
Odessa national academy of food
technologies,
112, Kanatnaja str., Odessa, Ukraine,
65039, tel. (0482) 29-11-26.
The
results of researches are expounded on the increase of protective properties of
unchroming surface of steel piston rings by oxidizing in a smouldering
discharge in the remaining atmosphere of air. The thickness
of oxide tapes concerned by an optical polarization method, phase composition
of oxide - method of electronic diffraction on the reflection. It is
investigational changing of electrode potentials, character of electrode
processes during external polarization and protective properties of oxide
tapes. By potential dynamic researches it is found out the region of passivity
in which the quantity of corrosive defeats at the test diminishes with 10 - 11
% to 0,2 - 0,3 %. It is found out the optimum regime
of treatment: 1000 V, 1,7 mÀ/ñm2, 10
minutes. A protective effect is predetermined by oxide tape of γ-Fe2O3, that is formed in a discharge.
Key words: tapes of oxides, corrosion, protective properties, ionic bombardment.
Full text (on original language).pdf (284kb)
I.S.
Manak, D.V. Ushakov, U.S. Bialiausky
Wide and Flat Waveguide Gain Spectrum
in the
Ga1-xInxAsySb1-y/AlxGa1-xAsySb1-y
Asymmetric Multiple-Quantum-Well Heterostructures
Belarussian State University,
Nezovisimosty av. 4, 220030, Belarus
Phone: 375 17 2781313, Fax: 375 17 2121016, e-mail: ushakovdv@bsu.by
For asymmetric
multiple-quantum-well heterostructures based on Ga1-xInxAsySb1-y/AlxGa1-xAsySb1-y
semiconductors it is shown that a wide and almost flat waveguide gain spectrum can
be obtained over the 2.3–2.84 mm spectral
range. Main attention is devoted to the results obtained under study of
spectral characteristics of two-, three- and four- quantum-well structures with
active region layers of different widths. Numerical simulation for band
diagrams of the active region and shape of the waveguide gain spectra are
performed.
Key words: Ga1-xInxAsySb1-y/AlxGa1-xAsySb1-y
heterostructure, multiple-quantum-wells, band diagram, inhomogeneous
excitation, wide waveguide gain spectra.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (287kb)
T.V. Cheban, O.M.
Beregova, A.I. Costrgitsckyy
Character of Energy Effects at the
Ion Plating of Sheeting
Îäåñüêà íàö³îíàëüíà àêàäåì³ÿ
õàð÷îâèõ òåõíîëîã³é,
êàôåäðà ô³çè÷íî¿ òà êîëî¿äíî¿ õ³ì³¿, âóë. Êàíàòíà, 112, ì.Îäåñà
The method of the ionic
precipitating is explained with possibility of substantial decline of
technological temperature of condensation. The calculation indexes of
temperature condition of steel (a thickness 4 ) are
resulted at treatment of surface in an argon and temperature condition of
precipitating of ionic coverage from a copper and ironchromical alloys on
steel. The analysis of power and temperature effects is conducted at the ionic
precipitating of coverage's.
keywords: corrosion, coverage, porosity,
ionic precipitating.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (213kb)
B.À. Tershak
Peculiarity of Aquation Activated
of Plugging Materials
Research
and planning institute VÀÒ «Ukrnafta»,
Pivnichnyy Bulvar named Pushkin’s, 4, Ivano-Frankivsk, 76019,
E-mail: tershak@ndpi.ukrnafta.com
The results of study of peculiarities
of plugging materials hydrated by excess pressure are given. The properties of plugging
muds formed such conditions have been researched. The mechanism of structure
formation of the given plugging material is studied. The perspectives of application
of mixture preparing method while well fixing are described.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (839kb)
M.M. Bobina, T.V. Loskutova, I.S. Pogrebova, À.V. Besov
Heat Resistant of Carbide Surface Coating on the Base of
Niobium and Chromium on the Carbon Steel Substrates
National
Technical University of Ukraine “KPI”, Peremogy Av., 37, Kyiv, 03056, Ukraine
The increasing of surface coating’s heat resistant for carbon steel after complex
doping by niobium and chromium are fixed. The numeric equations for high
temperature heat resistant time calculations are established.
Key words: heat resistant, niobium, chromium, surface coating, temperature.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (327kb)
Ì.Î. Yelizarov
Visualization by Method of
Khemografy Pitting
Corrosion of Metallic Tapes
Kremenchug state polytechnic university named by Ì.Ostrogradskyy
20, Pershotravneva Str. Kremenchug, UA-39614 Ukraine,
E-mail: yel@bigmir.net
An experimental
results of vizualization of corrosion processes
in metall – metall film systems are represent. An initial
stages of corrosion are vizualized for the first time, including the
local corrosion and the development of pitting particularly. This experiments
offer the challenge for further inquiry of corrosion processes in manifold
systems.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (1.17Mb)
A.
Cichon1, S. Borucki2
The Influence of Physical-Chemical
Parameters of Transformer Oil on the Time-Frequency Analysis Results of the
Acoustic Emission Signals Generated by Partial Discharges
1Technical
University of Opole, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Automatics,
ul. Sosnkowskiego 31, 45-272 Opole, Poland,
2Technical University of Opole, Institute of Electric Power Engineering,
ul. Sosnkowskiego 31, 45-272 Opole, Poland, e-mail acichy@po.opole.pl
The paper presents the measurement
results of the acoustic emission (AE) generated by partial discharges (PDs) in
oils of various physical-chemical parameters. The time-frequency analysis of
the AE signals measured for PDs generated in the particular oils was carried
out. For the AE signals measured, generated by PDs, the descriptors describing
a signal in the frequency domain were determined, amplitude spectra were drawn
and the spectrograms of the energy and amplitude density spectra were
determined.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (430kb)
M.Yu. Bobyk, V.P. Ivanitsky, O.V. Luksha
Improvement of Atomic Electronic
Amplitudes for Electron Diffraction
Technical Engineering
Departament, Uzhgorod National University,
Capitulna Str. 13, 88000 Uzhgorod, Ukraine. ivanc@mail.uzhgorod.ua
Using new coefficients of X-rays
scattering amplitudes of atoms are improved of atomic electronic amplitudes of
all elements the periodic table and many ions. Advantage of the received data
is an opportunity of the assignment of electronic amplitudes in a wide range of
scattering vectors. Comparison with known electronic amplitudes of different
atoms specifies a good correlation received and available results, and also
testifies about much higher precision and reliability of the improved data.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (273kb)
M.M. Ryaboschuk
Modeling of the Interference of Electron Waves Scattered on the Atomic
Pair of the Substance
Uzhgorod
national university, Uzhgorod, 13 Kapitulna str., tel.-614417, E-mail: ivanc@mail.uzgorod.ua
It was studied how the orientation
of the atomic pair of the substance relative to an electron ray influences the
general character of the distribution of interference intensity from the given
pair as well as the qualitative contribution of atomic pairs with different
orientation to the total diffraction pattern of the amorphous substance. It
follows from here that experimental electron-diffraction data reflect the
structure of amorphous substances which is predominantly characteristic for the
directions oriented relative to the probing ray at angles a = 40°…90°. The structure in the directions close to an incidence vector of
the probing ray is not actually reflected in them.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (380kb)
S.P. Novosyadlyy, R.Ì. Ivanyuk
Appreciation of Multi-Lamina
Metallization in the
Submicrons Structures of BIS
Vasyl
Stefanyk PreCarpathian National University,
57, Shevchenko Str., Ivano-Frankivsk,
76000, Ukraine
Explored
multi-lamina metallization on the basis of Al-Si-Ho-TiW, TiS2-TiN-TiW,
Ti+AKG0. It is shown that stability of the silicon integrated
submicrons schemes on the basis of Al metallization can be affined due to
balanced dispersion of warmth in the area of contact window. Determined optimum
correlation between the layers of AKGo and TiN, TiW, which allow to
create thermally stable submicrons structures on the basis of Al metallization
and to multiply heat emission from a crystal through internal bridges on the
external terminals of microshemes.
appreciation
of multi-lamina
metallization in the submicrons structures of BIS
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (560kb)
V.I.
Holota, I.T. Kohut
The Controlled Field Emission Silicic
Cathode of Sub-Micron Sizes on the Basis of SOI Structure
‘Vasyl Stefanyk’ Prekarpathian
National University,
201, Galytska Str., Ivano-Frankivsk, 76000, Ukraine,
E-mail: kre@pu.if.ua
The practical method of the
sub-micron sizes elements formation with the use of the standard projection
lithography is proposed. It is developed structure and topology of high-voltage
MOP transistor on SOI structure of that monolithically integrated with the
emitter and its electrical characteristics are obtained. It is developed the
technology of the production of the controlled field emission silicic emitters
of those integrated with SOI MOP transistor. It is proposed to use different
collections of images on the photo templates, which makes it possible on one
technology to form structures with the different profiles and sizes of
cathodes.
Full text (on original language)
.pdf (287kb)
![]() –function potentials. The distance
between the farthest atoms of the transitive layer is a parameter of the
problem and ranges from zero to two lattice parameters of crystals. An exact
solution is obtained for the reflection coefficient
–function potentials. The distance
between the farthest atoms of the transitive layer is a parameter of the
problem and ranges from zero to two lattice parameters of crystals. An exact
solution is obtained for the reflection coefficient ![]() which
makes it possible to determine the dependence of the factor on
a wave vector, widths of a transitive layer and a monolayer of the nanoheterostructure. The specific calculations performed for the
which
makes it possible to determine the dependence of the factor on
a wave vector, widths of a transitive layer and a monolayer of the nanoheterostructure. The specific calculations performed for the ![]() heterosystem showed
that the envelope-function approximation and the effective mass method at small values of a wave vector
yields quite good results provided the
heterosystem showed
that the envelope-function approximation and the effective mass method at small values of a wave vector
yields quite good results provided the